In today’s rapidly evolving business environment, understanding workforce structure is critical for legal compliance and operational success. One of the most important yet often misunderstood areas of HR management is employee classification. What Employers Need to Know About Employee Classification is a topic every employer must understand to avoid legal risks, financial penalties, and workplace disputes.
Understanding Employee Classification
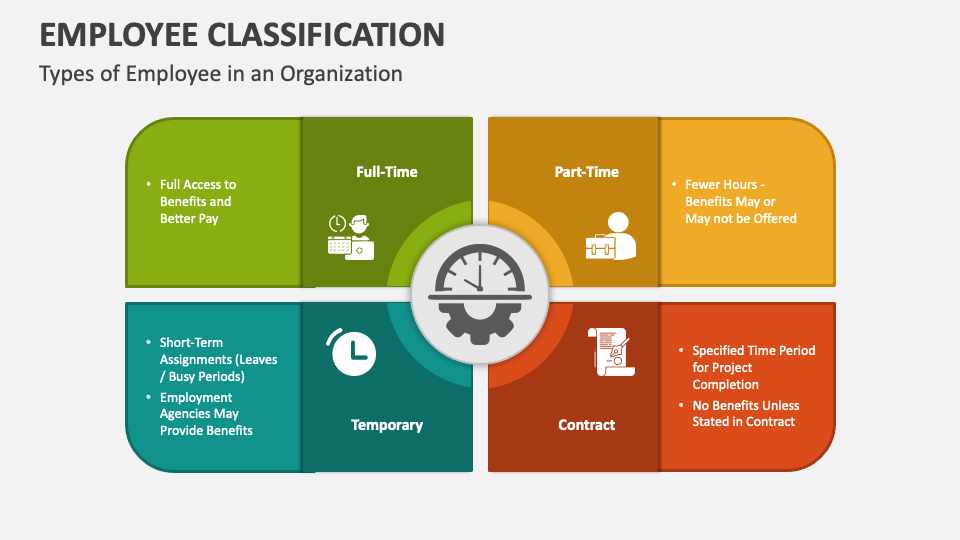
Employee classification refers to how workers are legally categorized based on the nature of their work, level of control, and relationship with the employer. Common classifications include full-time employees, part-time employees, independent contractors, temporary workers, and interns. Each category comes with specific legal rights, tax obligations, and benefits.
Misclassification can lead to serious consequences such as unpaid taxes, wage disputes, fines, and reputational damage. Therefore, employers must carefully evaluate how workers are classified and ensure compliance with applicable labor laws.
Why Employee Classification Matters for Employers
Proper employee classification is not just an administrative task—it directly impacts payroll, taxation, benefits, and legal liability. Employers who fail to classify employees correctly may face audits, lawsuits, or penalties from labor authorities.
Correct classification helps employers:
-
Maintain compliance with labor and tax laws
-
Avoid costly legal disputes
-
Ensure fair treatment of workers
-
Build trust and transparency in the workplace
Understanding what employers need to know about employee classification can significantly reduce business risks while promoting ethical employment practices.
Key Types of Employee Classifications
Full-Time Employees
Full-time employees typically work a standard number of hours per week and are entitled to benefits such as paid leave, health coverage, and retirement plans. Employers are responsible for withholding taxes and complying with employment laws for these workers.
Part-Time Employees
Part-time employees work fewer hours than full-time staff. While they may not receive the same benefits, employers are still required to comply with wage laws, tax obligations, and workplace safety regulations.
Independent Contractors
Independent contractors operate as self-employed individuals. Employers do not withhold taxes or provide benefits, but misclassifying an employee as a contractor can result in severe legal consequences. Control over work hours, tools, and methods often determines whether a worker qualifies as an independent contractor.
Temporary and Contract Workers
These workers are hired for a specific duration or project. While often managed through staffing agencies, employers must still understand their legal responsibilities, especially regarding workplace safety and fair treatment.
Common Employee Misclassification Mistakes
One of the most common mistakes employers make is treating workers as independent contractors when they function as regular employees. This usually happens to reduce costs associated with taxes and benefits, but it often leads to legal issues.
Other common mistakes include:
-
Assuming job titles determine classification
-
Ignoring working hours and supervision levels
-
Failing to update classification as roles change
-
Misunderstanding local labor laws
Knowing what employers need to know about employee classification helps prevent these errors and ensures long-term compliance.
Legal and Financial Risks of Misclassification
Employee misclassification can result in:
-
Back payment of wages and overtime
-
Tax penalties and interest
-
Legal claims from workers
-
Government audits and investigations
In some cases, employers may also face criminal charges for repeated or intentional violations. These risks make it essential for businesses to regularly review and correct their employee classifications.
How Employers Can Ensure Proper Classification
To avoid misclassification, employers should take proactive steps, including:
-
Reviewing job roles and responsibilities carefully
-
Understanding labor laws and employment standards
-
Consulting HR and legal professionals
-
Conducting regular workforce audits
-
Maintaining accurate documentation
Clear contracts, transparent policies, and proper onboarding processes also play a key role in ensuring correct employee classification.
Employee Classification in a Changing Workforce
With the rise of remote work, freelancing, and gig-based employment, employee classification has become more complex. Employers must adapt to new working models while staying compliant with labor regulations.
Remote workers, for example, may still qualify as employees depending on how much control the employer exercises. Employers must evaluate each role individually rather than relying on outdated assumptions.
Best Practices for Employers
To stay compliant and avoid disputes, employers should:
-
Educate HR teams on employment laws
-
Regularly review classification criteria
-
Communicate clearly with workers about their status
-
Update contracts when roles evolve
-
Seek professional guidance when in doubt
Implementing these best practices ensures fair treatment of workers while protecting the business from unnecessary risks.
Conclusion!
Employee classification is a critical aspect of workforce management that every employer must take seriously. Understanding what employers need to know about employee classification helps businesses stay compliant, reduce legal exposure, and foster a fair and transparent work environment.
By accurately classifying workers, staying informed about labor laws, and adopting best practices, employers can build sustainable operations while protecting both their business interests and employee rights.







